Acetic acid is a versatile chemical intermediate used in a variety of products such as paints, adhesives and solvents as well as in the production of PTA for polyester manufacture. BP has developed a new process for a production of Acetic Acid (AA) from syngas through multistep reactions that is called BP-SaaBre process. This process has advantages compared with conventional homogeneous AA production processes (liquid-phase carbonylation of methanol) by eliminating a separation problem of homogeneous precious metal complexes (catalyst) from corrosive liquid products containing expensive and exotic halides. Therefore, BP-SaaBre process seems to be more economically feasible than other commercialized processes for a liquid phase carbonylation reaction with homogeneous catalysts.
Historically, Haldor Topsoe had firstly proposed similar integrated processes that include a synthesis of methanol and dimethyl ether (DME or CH3OCH3) from syngas and a subsequent carbonylation of DME to AA in a gas-phase. In other words, the syngas can be converted to AA in the following four steps:
CO + 2H2 —> CH3OH
2CH3OH —> CH3OCH3 + H2O
CH3OCH3+CO —> CH3COOCH3
CH3COOCH3 + H2O —> CH3OH + CH3COOH
The BP-SaaBre process seems to be composed of the following three main reactors as shown in Figure 15:
- CO hydrogenation to methanol and methanol dehydration to DME
- DME Carbonylation to methyl acetate (MA) and MA dehydration
- MA Hydrolysis to an equal molar AA and methanol.
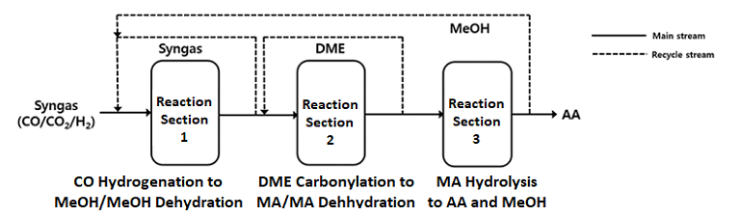
Figure 15: Reaction schemes of the BP-SaaBre process with three separate gas-phase reaction sections
The unreacted syngas from the exit of reactor 1, DME from the reactor 2 and methanol by-product from the reactor 3 can be separately recycled to the previous reactor for increasing carbon efficiency of the BP-SaaBre process.
BP is progressing with plans to build a 1 million tonnes per year acetic acid plant in Oman using natural gas as feedstock to produce syngas. There is no reference for waste to acetic acid plan although there is reference plant for waste to syngas and BP SaaBre technology is demonstrated in BP facilities in the UK.
As per reactions shown below including gasification of MSW, water-gas shift reaction, methanol formation reaction, methanol dehydration to DME, DME carbonylation to methyl acetate and methyl acetate hydrolysis, waste to fuel technology produce less CO2 than WtE, WtH and WtM technologies:
CO + H2O —> CO2 + H2
CO + 2H2 —> CH3OH
2CH3OH —> CH3OCH3 + H2O
CH3OCH3+CO —> CH3COOCH3
CH3COOCH3 + H2O —> CH3OH + CH3COOH
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
7CO + 4H2O —> 4CO2 + CH3COOH + CH3OH
or CO + 0.5714H2O —> 0.5714CO2 + 0.1429CH3COOH + 0.1429CH3OH